Specific Steam Consumption of Ideal Rankine Cycle
Thermal efficiency of a practical Rankine cycle. Work input to feed pump W P 302 kJkg.
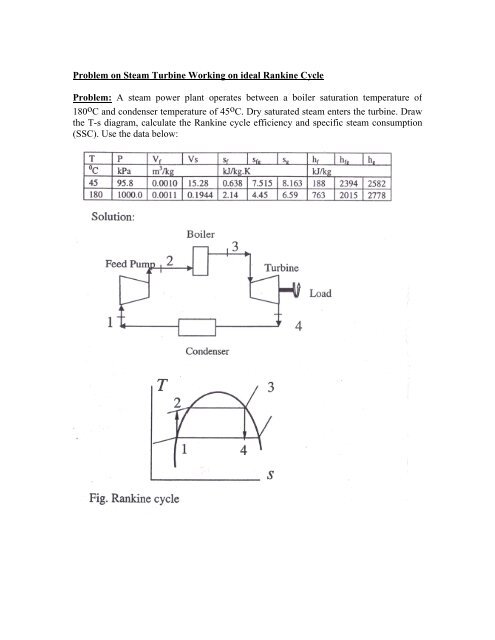
Problem On Steam Turbine Working On Ideal Rankine Cycle
η W net Q in 1 Q out Q in.

. Heat rejected to the condenser Q 2 176132 kJkg. Therefore all important parameters of water and steam are tabulated in so-called Steam Tables. 9 Energy Analysis of the Ideal Rankine Cycle Specific steam consumption ssc is the steam flow in kgh required to develop 1 kW ssc3600Wnet KgKjh The thermal efficiency can be interpreted as the ratio of the area enclosed by the cycle on a T-s diagram to the area under the heat-addition process.
The basic Rankine cycle is presented in terms of temperature and entropy change in Figure 102. C Power Developed m s x Work done per kg 160 h 1 - h 2 160 11516 184256 kW 184256 MW d Specific steam consumption 3600 h 1 - h 2 3600 11516. In the Fundamental Design Calculations for the 5AT see FDC 13 Wardale gives figures of minimum indicated Specific Steam Consumption for the Duke of Gloucester as 122 lbhp-h and for the SNCF 141P Class 4-cyl.
In the actual turbine the work delivered is less than the isentropic turbine. A steam power plant operates on an ideal Rankine cycle between a boiler pressure of 40 bar 300C and a condenser pressure of 0035 bar. By condensing the working steam to a liquid.
H T a - T r T a 2267 - 458 226727315 362 Which is the same answer we get applying the usual h W net Q hi relation. In the case of the Rankine cycle the Ideal Gas Law almost cannot be used steam does not follow pVnRT. It is defined as the mass of steam required per unit power output.
Constant pressure heat addition in a boiler. One of the major advantages of the Rankine cycle is that the compression process in the pump takes place on a liquid. The simple ideal Rankine cycle.
Derive an expression for efficiency of the Rankine cycle. A A Carnot cycle using wet steam W h h 27996 180902 99058 kJ kg h h x h 1118 0696 243853 180902kJ kg h 1118 kJ kg. Rankine engine efficiency is about equivalent to Rankine efficiency.
Do not neglect pump work. To improve the efficiency of Rankine cycle in the steam power plant there are some changes in Rankine cycle which differs from the Carnot cycle. By condensing the working steam to a liquid.
Calculate the work output heat input cycle efficiecy and specific steam consumption of an ideal Rankine cycle steam power plant with a boiler pressure of 2 Mpa a condenser pressure of 10 kPa and a boiler exit temperature of 400C. A steam power plant operates on a simple ideal Rankine cycle between the specified pressure limits. A Carnot cycle using steam as a working substance is represented or p-v and t-s diagram as shown in the figure.
Similarly the work consumed by an actual pump is greater than the work consumed by an isentropic pump. The Rankine Cycle is a mechanical cycle commonly used in power plants to convert the pressure energy of steam into mechanical energy through steam turbines. As a quick check we can find the Rankine cycles thermal efficiency by applying the relation for Carnot efficiency to the mean Rankine cycle temperatures.
Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. In a steam power plant operating on ideal Rankine cycle steam enters the turbine at 20 bar with an enthalpy of 3384 kJkg and an entropy of 7127 kJkg K. Answer below.
H 255033kJ kg h 255033 1118 243858 kJ kg x 0696 605 0391 x 813 where s 85223kJ kg 85223 0391 813kJ kg s s x s h 27996 kJ kg s s s s 605kJ kgK refer steam table Assume. The ideal Rankine cycle does not have any internal irreversibility. Rankine cycle is nothing but a modification of Carnot cycle.
The specific steam consumption is kgkWh round off to 2 decimal places. The ideal state of this cycle is reflected in the vertical lines 1-2 and 3-4 when the fluid compressed and expanded. Consider 1kg of water at pressure P1 and absolute temperature T1 as represented by.
KgkW-hrSSC For an ideal Rankine cycle operating between pressures of 30 bar and 004 bar the work output from the turbine is 903 kJkg and the work input to the feed pump is 3 kJkgThe specific steam consumption is _________________ kgkWh round off to 2 decimal. For an ideal Rankine cycle operating between pressures of 30 bar and 004 bar the work output from the turbine is 903 kJkg and the work input to the feed pump is 3 kJkg. Specific steam consumption Steam flow kgh Power.
Work output of turbine W T 86070 kJkg. 2 Kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible. The Rankine cycle is a modified form of Carnot cycle in which the isothermal compression 3-4 is continued unit the steam is condensed into water.
Firstly a pump is used in place of condenser to handle only liquid not a mixture of liquid and. WDturbine 903 kJkgWDpump 3 kJkgSpecific steam consumption. Apr 04 2021 1119 AM.
The thermal efficiency of the cycle the mass flow rate of the steam and the temperature rise of the cooling water are to be determined. That is h 3-h 4 h 3-h 4. The practical Rankine cycle is shown as 1-2-3-4-1.
One of the major advantages of the Rankine cycle is that the compression process in the pump takes place on a liquid. Find the cycle efficiency and specific steam consumption in kgkWh. Therefore in Rankine cycle efficiency the pump work is ignored.
Therefore all important parameters of water and steam are tabulated in so-called Steam Tables. The Rankine cycle is the ideal cycle for vapor power plants. How this cycle is different from the Carnot cycle.
Calculate cycle efficiency work ratio and specific steam consumption for a Ideal Rankine cycle b For Rankine cycle when expansion process has an isentropic efficiency of 80. By condensing the working steam to a liquid. Calculate the heat and work transfers of an ideal saturated Rankine cycle using steam between pressures 3 MPa and 867 kPa.
In the case of the Rankine cycle the Ideal Gas Law almost cannot be used steam does not follow pVnRT. Ideal Rankine cycle is very useful in steam power plants and gas power plants. One of the major advantages of the Rankine cycle is that the compression process in the pump takes place on a liquid.
In case of the Rankine cycle the Ideal Gas Law almost cannot be used steam do not follow pVnRT therefore all important parameters of water and steam are tabulated in so called Steam Tables. A boiler is used to heat the water for steam at the required. Thermodynamic analysis of cycle.
The specific steam consumption SSC. Therefore the thermal efficiency of this cycle can be presented as follows. H 2 -h 1 h 2-h 1.
The Rankine Cycles major components include a rotating steam turbine a boiler pump a stationary condenser and a boiler. Define specific steam consumption of an ideal Rankine cycle. Heat added in the steam generator Q 1 261900 kJkg.
The condenser pressure is 015 bar. W q 16992 04304 73134. Compound 2-8-2 as 112 lbhp-hr as compared to 1124 lbhp-h 51 kghp-hr or 19 kgMJ for the 5AT.
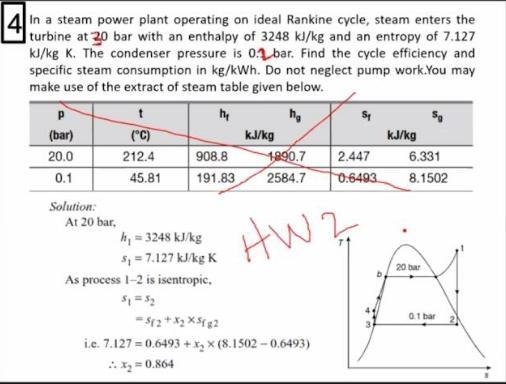
Solved 4 Of In A Steam Power Plant Operating On Ideal Chegg Com

Rankine Cycle Introduction Youtube

Specific Steam Consumption Steam Rate Heat Rate Engineering Thermodynamics 118 Youtube
No comments for "Specific Steam Consumption of Ideal Rankine Cycle"
Post a Comment